|
Variants of the "stage and a half" drive
system (MA) of the Atlas rocket
Norbert Brügge, Germany
Unwilling to take the risk of building a multistage
missile that might later prove unworkable, Convair built the Atlas rocket
around its unique "stage-and-a-half" propulsion system.
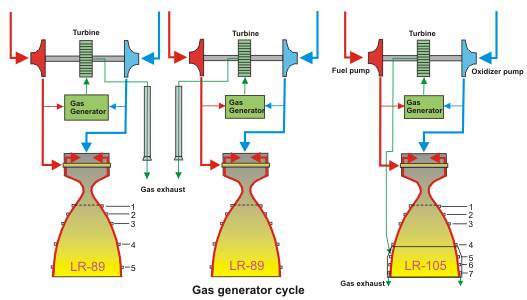
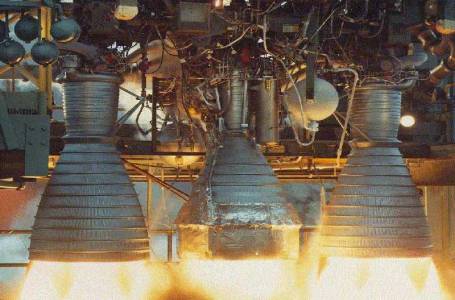
This "stage-and-a-half" propulsion system in which
three engines – two boosters and a sustainer engine – are fed by the same
liquid oxygen/RP-1 (kerosine mixture) propellant tanks and all ignited at
liftoff. During the first few minutes of flight, the boosters shut down and
fall away (to save weight), while the sustainer continues burning.
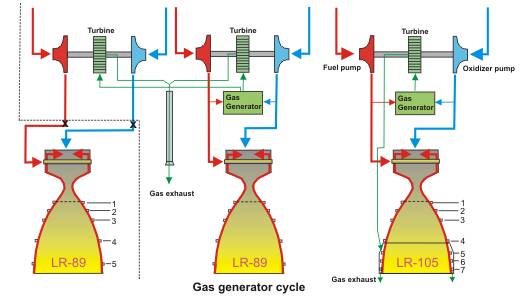
The two booster engines LR-89 were developed by Rocketdyne.
Combustion chamber and nozzle were made by nickel welded tubes. Characteristic
of the MA-1, MA-2; MA-3 and MA-5 systems are different drive combinations
of the two LR-89 engines:
-
MA-1:
Both engines are powered centrally by one set of turbo pumps with gas generator.
-
MA-2:
Both engines are powered by own set of turbopumps. All turbo pumps are driven
by a single gas generator, which are located at one of the engines.
-
MA-3:
Both engines are powered by own set of turbo pumps and gas generator.
-
MA-5:
Both engines are powered by two sets of turbo pumps with a common gas generator.
All turbo pumps are arranged at one of the engines.
-
MA-5A:
Both engines (new RS-27 combustor) are powered by two sets of turbo pumps
with a common gas generator. All turbo pumps are arranged at one of the
engines.
A new development was the central engine LR-105 (Sustainer).
The thrust was lower, but it was the first engine, which was specifically
designed to operate in a vacuum. It had a higher outflow velocity than the
two booster engines. The gas turbine with its own gas generator operates at
a high rotational speed of 10,800 rev / min (Booster only 6.300 U / min).
The central engine could be swung on gimbals in two axes by 3 degrees. The
burning time of the LR-105 varied depending of the time of dropping the booster
engines.
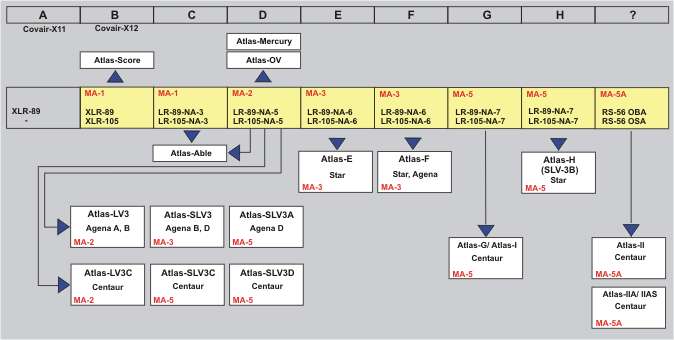
The variants of the MA drive system and their
use.
|
MA-0 |
|



Convair SM-65A (Atlas-A)
|

|
The Convair
SM-65A was the first testbed and was developed into the Atlas-A. The Atlas-A
flights were powered by a single engine consisting of two thrust chambers
XLR-89 fed by a single set of turbopumps.
The central sustainer engine XLR-105 still missing.
|
Engine
|
Other
Design
|
Chamb.
|
Nozzle
Area Ratio
|
Press.
Exp. Ratio
|
Chamb. Press.
(MPa)
|
Propellants
|
Stage
|
Oxid.
Mix Rate
|
Thrust s.l.
|
Isp s.l.
|
Thrust vac.
|
Isp vac
|
Flow Rate
(t/sec)
|
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
|
XLR-89-1
|
MA-0
|
2x1
|
|
|
|
RP-1/LOX
|
Booster
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Sustainer
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
MA-1 |
|



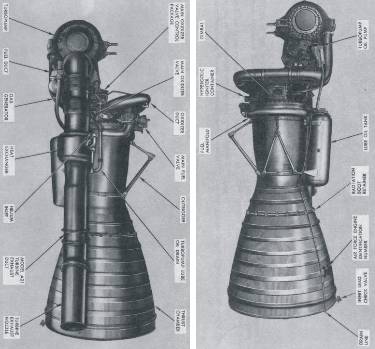
Convair SM-65B (Atlas-B)
The Convair SM-65B was
the second, more advanced testbed for the Atlas rocket program. It was
designed with 2 engines, the booster engine XLR-89 used on the predecessor
SM-65A plus a sustainer engine XLR-105. This combination of booster plus
sustainer engines was designated the MA-1 engine system. MA-1 was
used in Atlas-B and first series of Atlas-C.
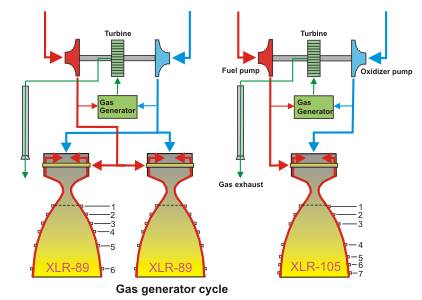
|


(X)LR-105 combustor
|
|
Engine
|
Other
Design
|
Chamb.
|
Nozzle
Area Ratio
|
Press.
Exp. Ratio
|
Chamb. Press.
(MPa)
|
Propellants
|
Stage
|
Oxid.
Mix Rate
|
Thrust s.l.
|
Isp s.l.
|
Thrust vac.
|
Isp vac
|
Flow Rate
(t/sec)
|
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
|
LR-89-NA-3
|
MA-1
|
2x1 |
|
|
|
RP-1/LOX |
Booster
|
2.25 |
1,316.7 |
248.0 |
2432 |
1,497.3 |
282.0 |
2765 |
0.5414 |
|
LR-105-NA-3
|
1
|
|
|
|
Sustainer
|
2.27 |
244.7 |
215.0 |
2108 |
352.2 |
309.0 |
3030 |
0.1166 |
|
|

XLR-89 engine
|

XLR-105 engine (no aspirator !)
|
|
MA-2 |
|

LR-89-NA-5
|

LR-105-NA-5 exaust tube
|
|

Atlas-D/Mercury
|
Atlas-C/Able
|
|
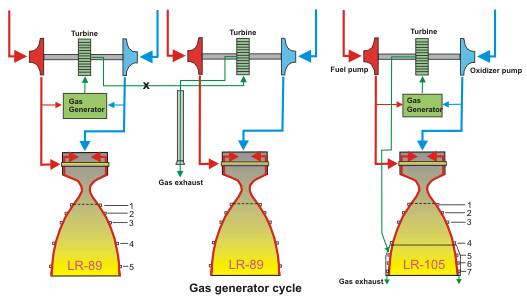
|

|
|
Engine
|
Other
Design
|
Chamb.
|
Nozzle
Area Ratio
|
Press.
Exp. Ratio
|
Chamb. Press.
(MPa)
|
Propellants
|
Stage
|
Oxid.
Mix Rate
|
Thrust s.l.
|
Isp s.l.
|
Thrust vac.
|
Isp vac
|
Flow Rate
(t/sec)
|
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
|
LR-89-NA-5
|
MA-2
|
2x1 |
|
8 |
3.92 |
RP-1/LOX |
Booster
|
2.25 |
1,334.5 |
248.0 |
2432 |
1,517.4 |
282.0 |
2765 |
0.5487 |
| LR-105-NA-5 |
1
|
|
25 |
4.41 |
Sustainer
|
2.27 |
253.1 |
215.0 |
2108 |
366.1 |
311.0 |
3050 |
0.1200 |
|
|
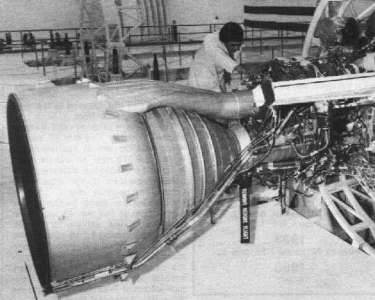
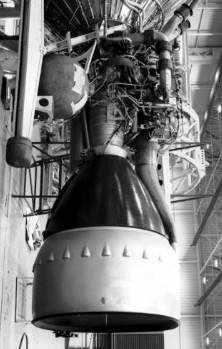
MA-3 |
|

|
|


Atlas-E/F ICBM
|

|
|


|
|
Engine
|
Other
Design
|
Chamb.
|
Nozzle
Area Ratio
|
Press.
Exp. Ratio
|
Chamb. Press.
(MPa)
|
Propellants
|
Stage
|
Oxid.
Mix Rate
|
Thrust s.l.
|
Isp s.l.
|
Thrust vac.
|
Isp vac
|
Flow Rate
(t/sec)
|
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
|
LR-89-NA-6
|
MA-3
|
2x1 |
|
8 |
4.04 |
RP-1/LOX |
Booster
|
2.25 |
1,467.9 |
256.0 |
2510 |
1,662.8 |
290.0 |
2844 |
0.5847 |
| LR-105-NA-6 |
1
|
|
25 |
4.71 |
Sustainer
|
2.27 |
253.1 |
215.0 |
2108 |
366.1 |
311.0 |
3050 |
0.1200 |
|
|
|

LR-89-NA-6
|
|


|
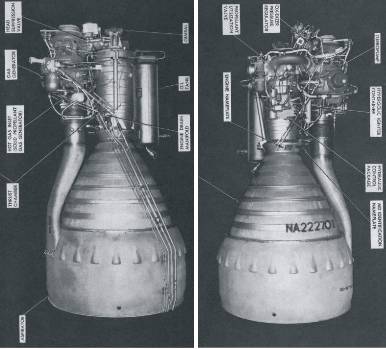
LR-105-NA-6; Openings in
the aspirator are different
|
|
|
|
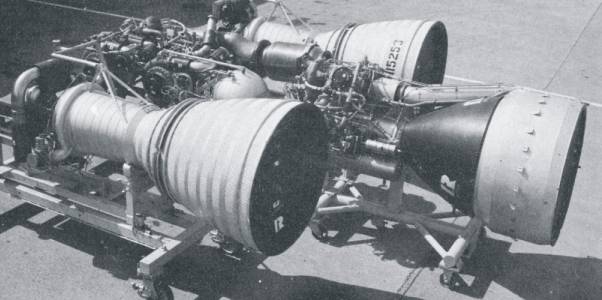
MA-5 |
|

Atlas-G/Centaur
|

LR-105-NA-7
|
|
|

LR-89-NA-7
(On this part: two sets of turbo pumps and a common gas generator)
|
|
|

|
|
Engine
|
Other
Design
|
Chamb.
|
Nozzle
Area Ratio
|
Press.
Exp. Ratio
|
Chamb. Press.
(MPa)
|
Propellants
|
Stage
|
Oxid.
Mix Rate
|
Thrust s.l.
|
Isp s.l.
|
Thrust vac.
|
Isp vac
|
Flow Rate
(t/sec)
|
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
|
LR-89-NA-7.1
|
MA-5.1
|
2x1 |
|
8 |
4.12 |
RP-1/LOX |
Booster
|
2.25 |
1,645.9 |
258.0 |
2530 |
1,863.4 |
292.2 |
2865 |
0.6505 |
| LR-105-NA-7.1 |
1
|
|
25 |
4.80 |
Sustainer
|
2.27 |
268.7 |
220.4 |
2161 |
385.2 |
316.0 |
3099 |
0.1243 |
|
LR-89-NA-7.2
|
MA-5.2
|
2x1 |
|
8 |
4.12 |
RP-1/LOX |
Booster
|
2.25 |
1,679.2 |
259.1 |
2541 |
1,901.6 |
293.4 |
2877 |
0.6609 |
| LR-105-NA-7.2 |
1
|
|
25 |
4.80 |
Sustainer
|
2.27 |
269.1 |
220.0 |
2157 |
386.4 |
316.0 |
3099 |
0.1243 |
|
| |
|
MA-5A |
|

|

Atlas-IIAS
|
|
|

|
|
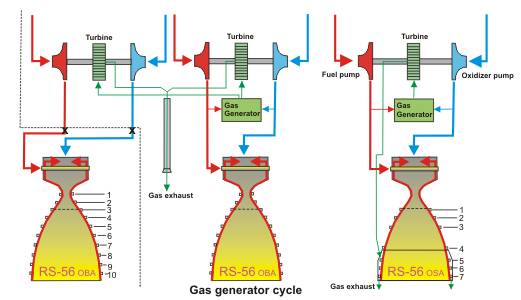
|

RS-56 OBA combustor (RS-27
derivative)
|
|
Engine
|
Other
Design
|
Chamb.
|
Nozzle
Area Ratio
|
Press.
Exp. Ratio
|
Chamb. Press.
(MPa)
|
Propellants
|
Stage
|
Oxid.
Mix Rate
|
Thrust s.l.
|
Isp s.l.
|
Thrust vac.
|
Isp vac
|
Flow Rate
(t/sec)
|
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
kN
|
sec
|
Ns/kg
|
|
RS-56
OBA
|
MA-5A
|
2x1 |
|
8 |
4.71 |
RP-1/LOX |
Booster
|
2.25 |
1,906.0 |
262.1 |
2570 |
2,155.2 |
296.4 |
2907 |
0.7415 |
| RS-56
OSA |
1
|
|
25 |
5.07 |
Sustainer
|
2.27 |
268.6 |
220.4 |
2161 |
385.2 |
316.0 |
3099 |
0.1243 |
|
|
|
|












































